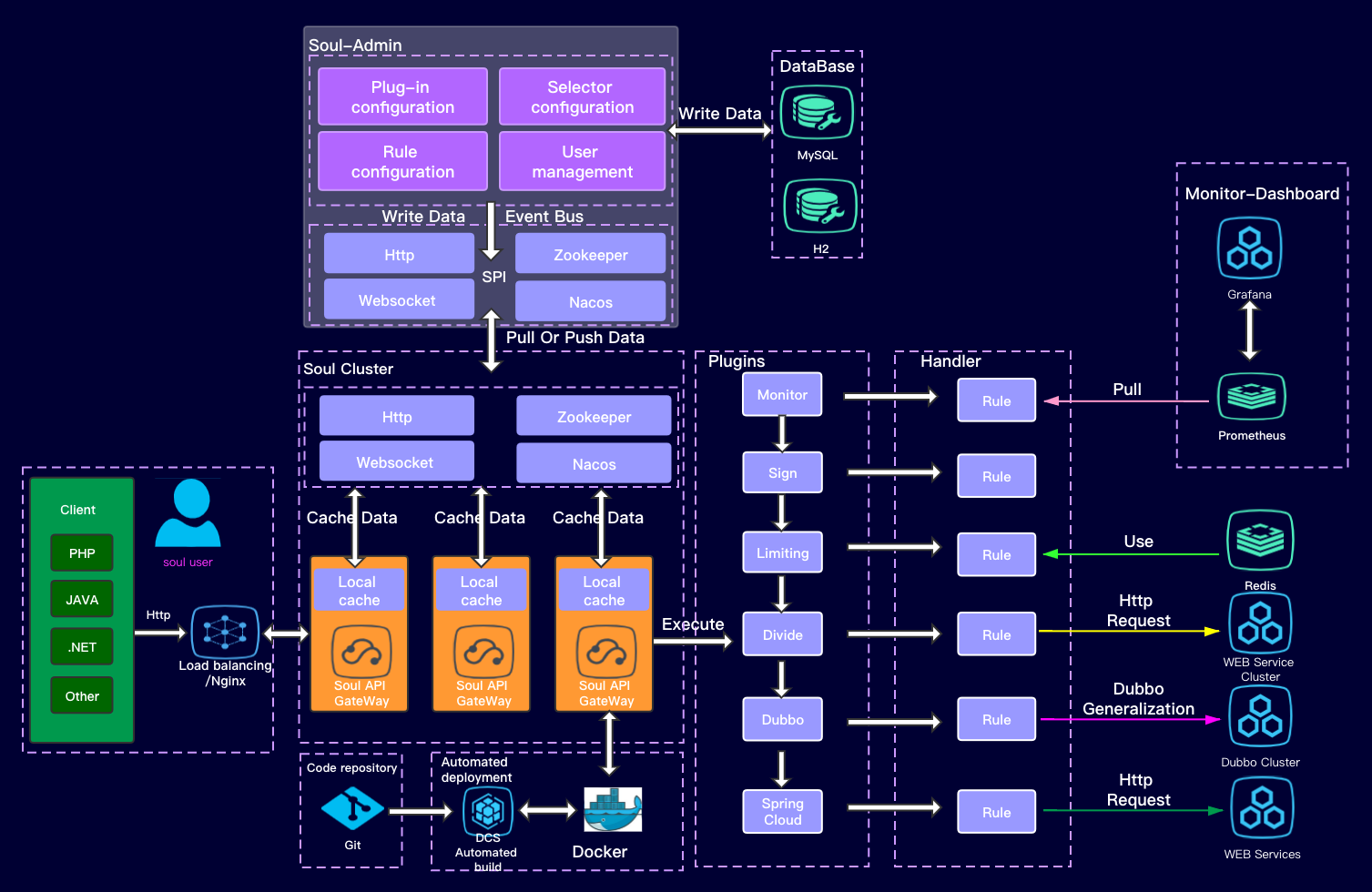
Soul Gateway Learning Sign Plugin
Introduction
The sign plug-in is used to sign and authenticate requests.
AK/SK Introduction
AK/SK (Access Key ID/Secret Access Key) is the access key, including the access key ID (AK) and the secret access key (SK), which is mainly used to authenticate and authenticate the user's calling behavior.
Plugin usage-take (/dubbo/findAll) as an example
Support added sign in SoulBootstrap's POM. XML films
<!-- soul sign plugin start-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>soul-spring-boot-starter-plugin-sign</artifactId>
<version>${last.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- soul sign plugin end-->Add appKey, secretKey
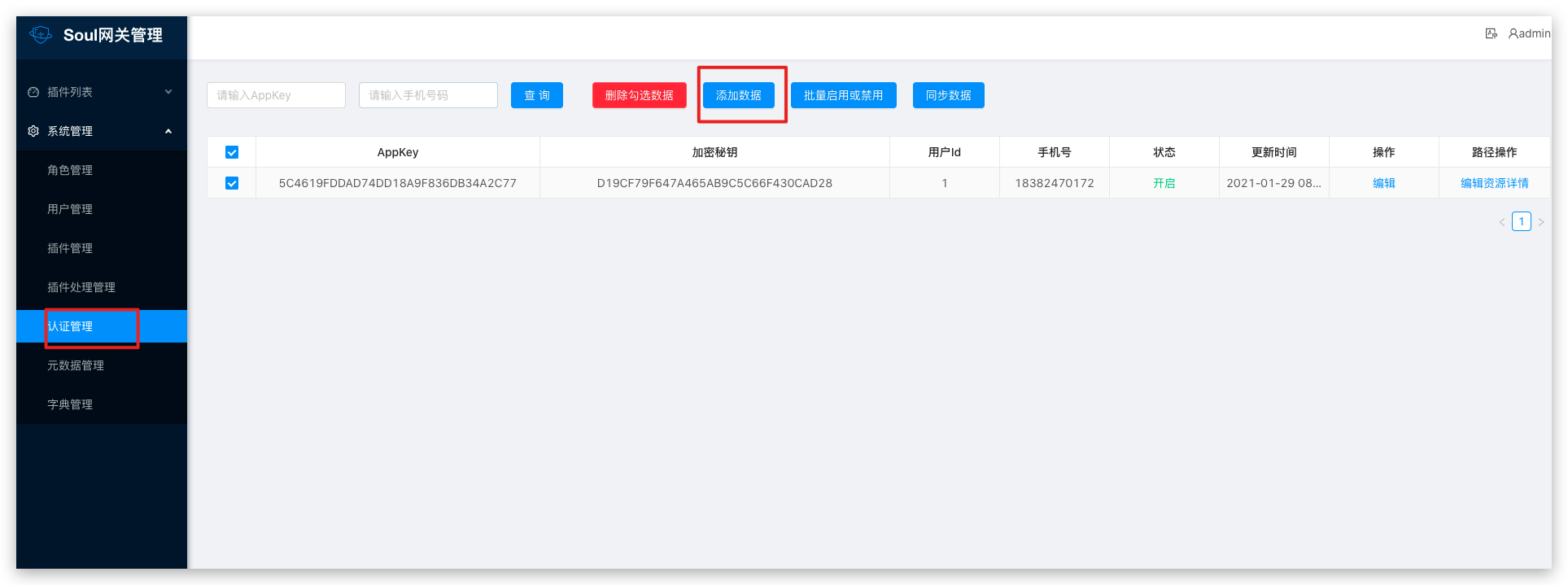
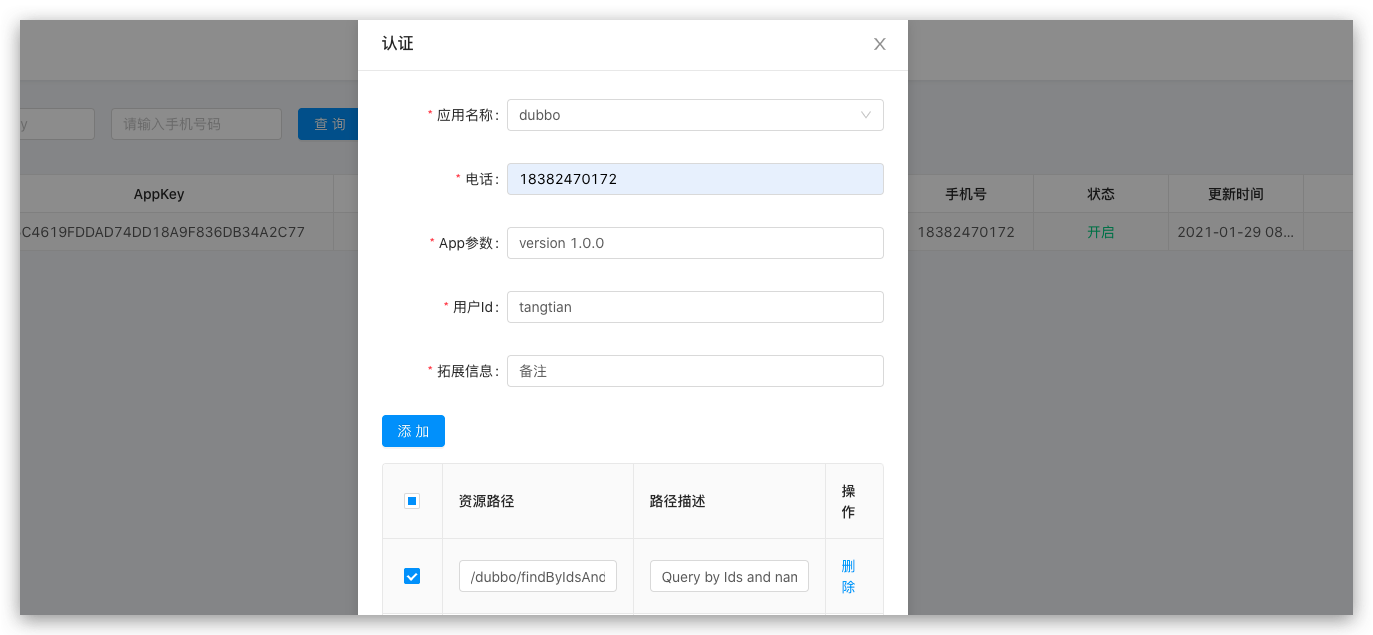
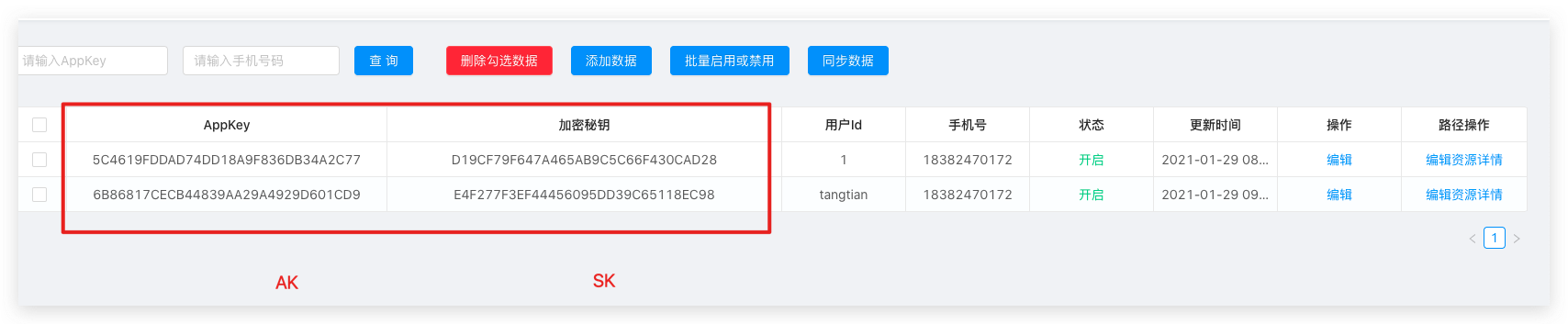
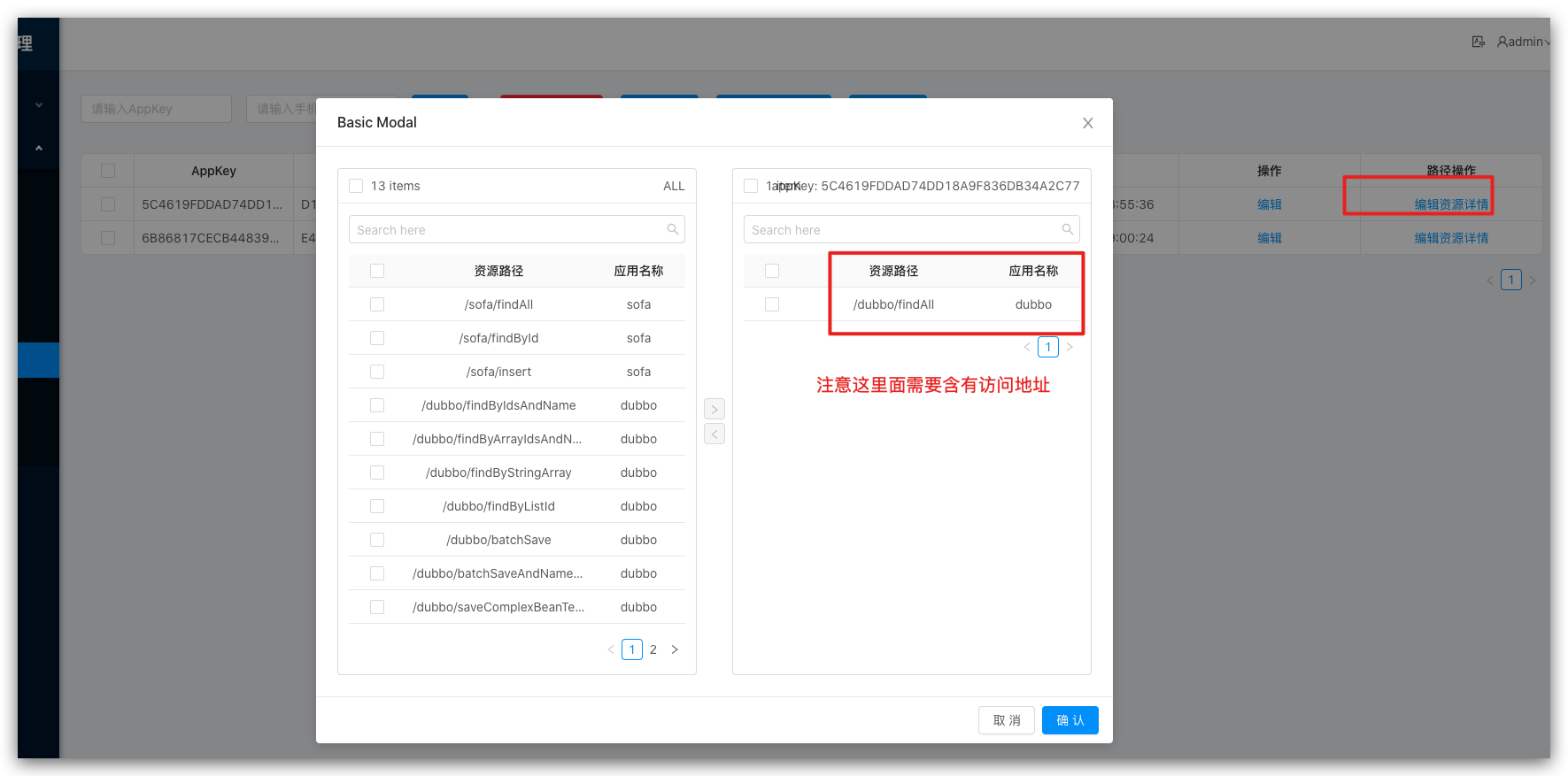
Configure Selectors and Regulators
Add Selector 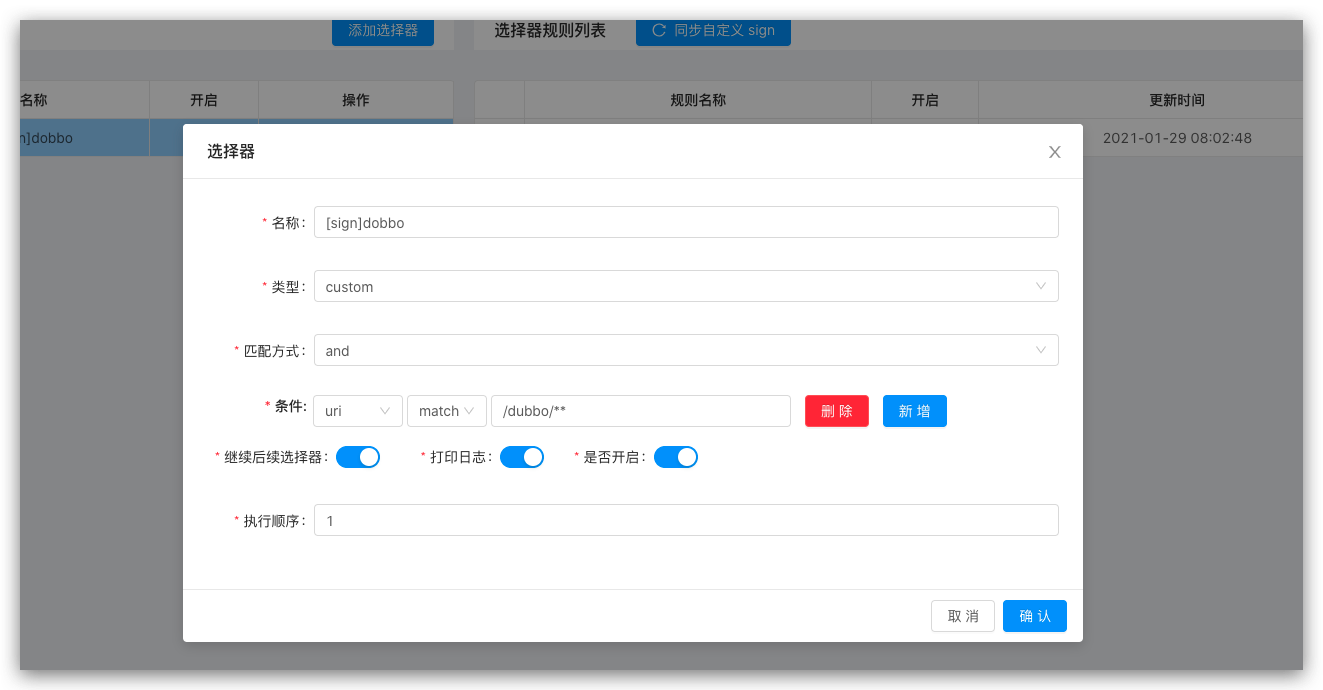 Add Ruler
Add Ruler 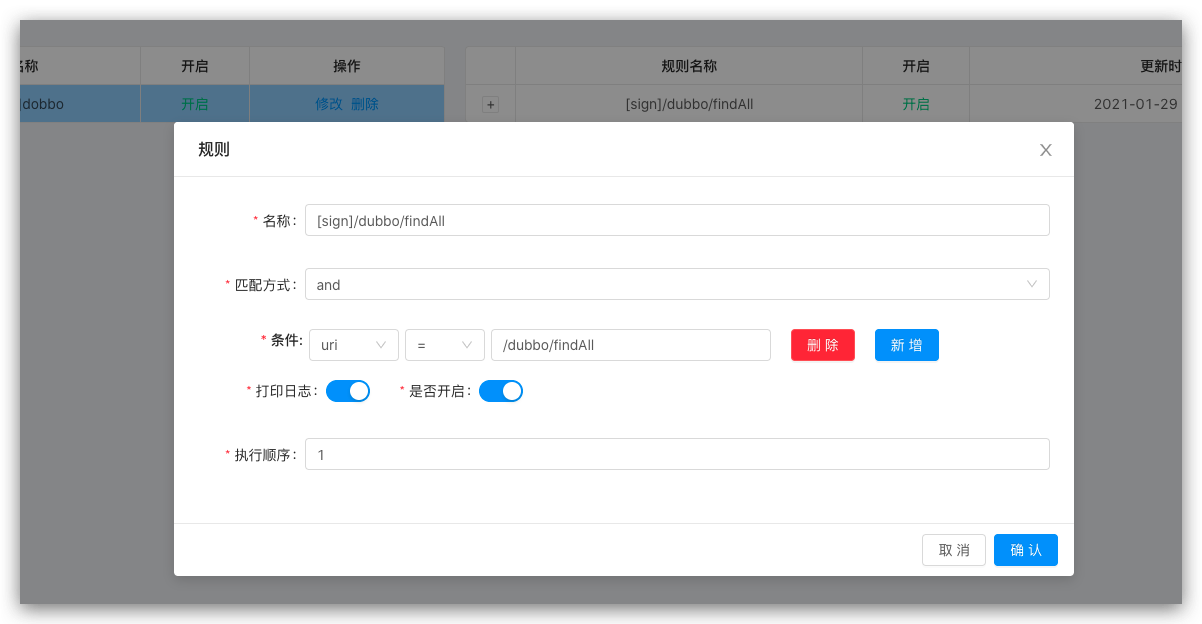
Add the service of obtaining authentication
Add an external access method to your service
@GetMapping("/authUrl")
public String authUrl() {
Map<String, String> map = Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(2);
//Convert timestamp to string form of milliseconds: String.valueOf(LocalDateTime.now().toInstant(ZoneOffset.of("+8")).toEpochMilli())
String timetamp = String.valueOf(LocalDateTime.now().toInstant(ZoneOffset.of("+8")).toEpochMilli()) ;
System.out.println(timetamp);
map.put("timestamp",timetamp); //The value should be in the form of a string representing milliseconds
map.put("path", "/dubbo/findAll");
map.put("version", "1.0.0");
List<String> storedKeys = Arrays.stream(map.keySet()
.toArray(new String[]{}))
.sorted(Comparator.naturalOrder())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
final String sign = storedKeys.stream()
.map(key -> String.join("", key, map.get(key)))
.collect(Collectors.joining()).trim()
.concat("D19CF79F647A465AB9C5C66F430CAD28");//SECRETkey
return DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(sign.getBytes()).toUpperCase();
}The following should be noted 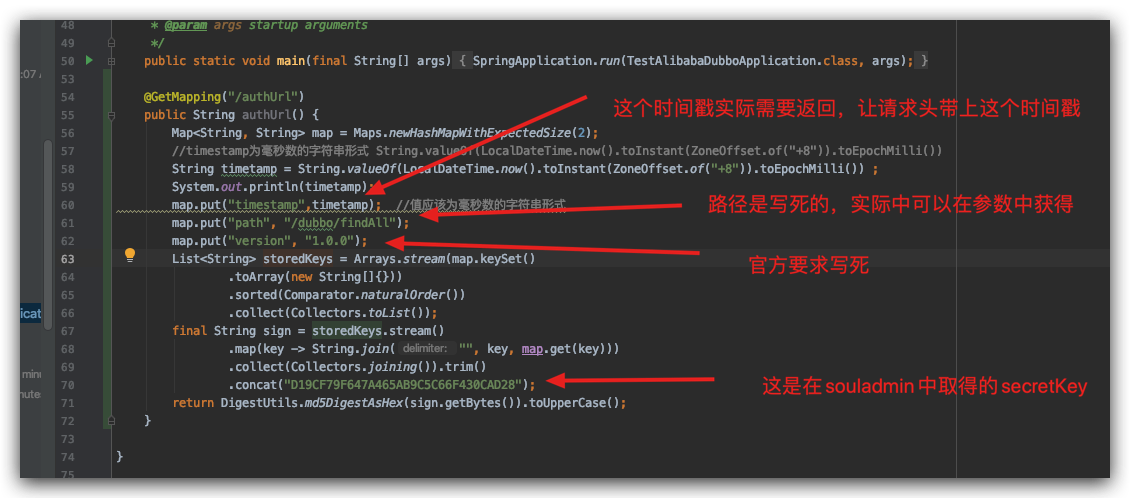
Adding authentication header information in the gateway
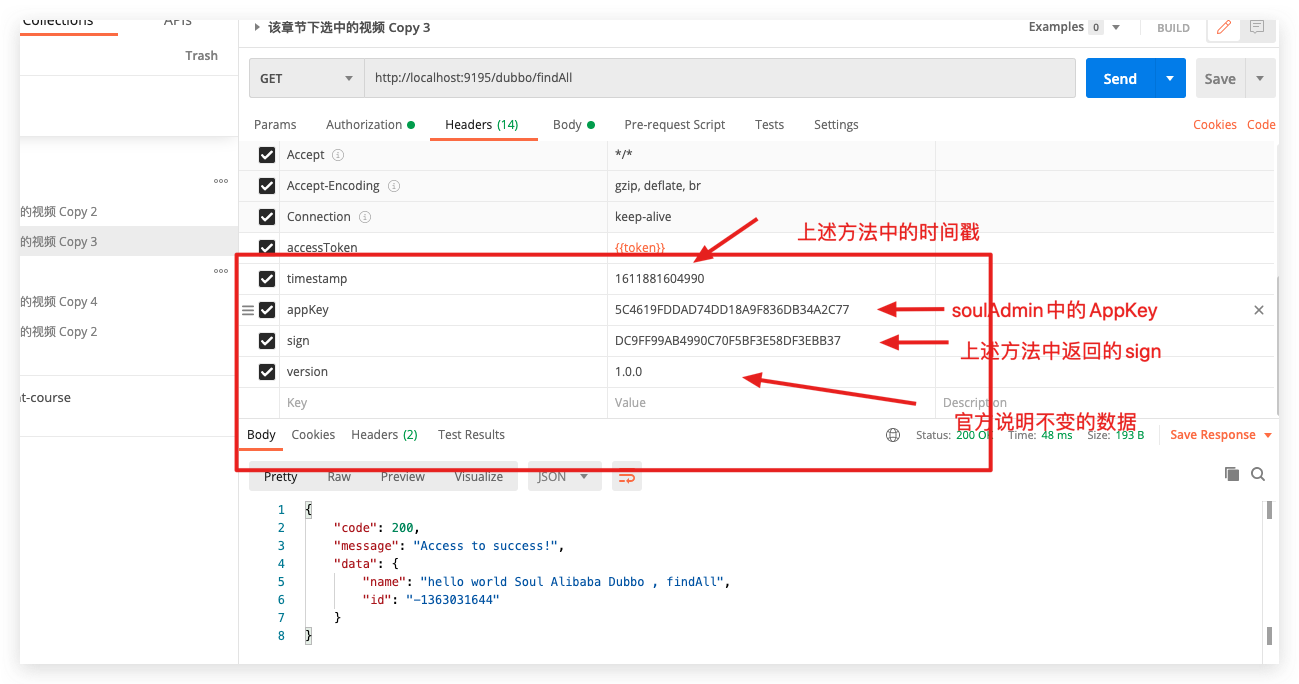
Demo of the requested result
Passed return 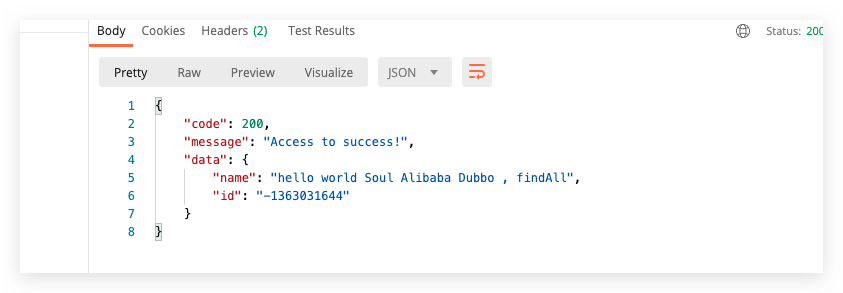 5min timeout return
5min timeout return 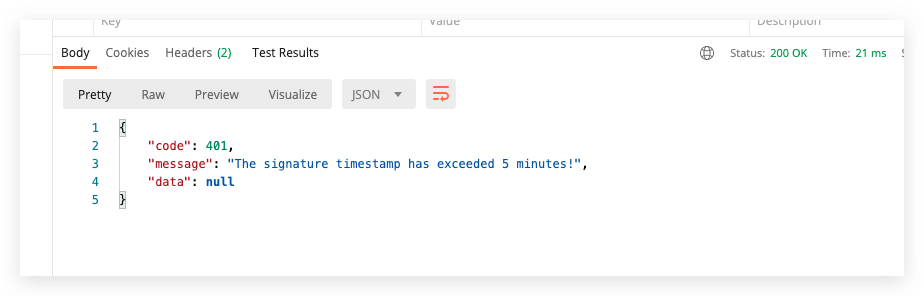 appKey filling error return
appKey filling error return 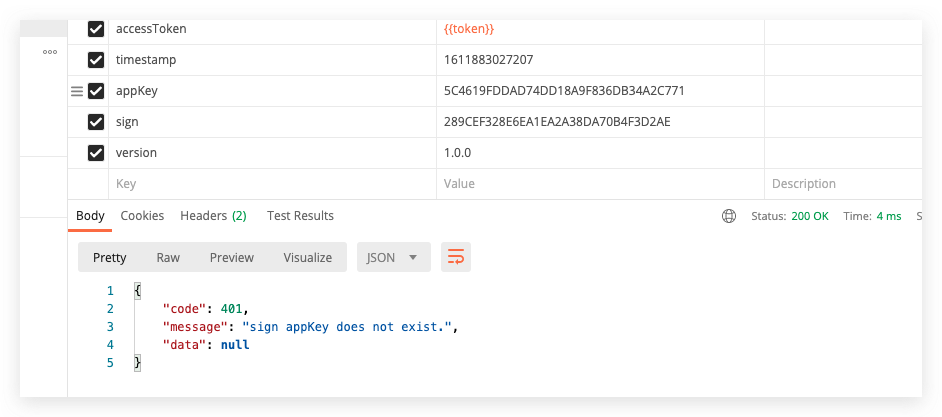 signature error return
signature error return 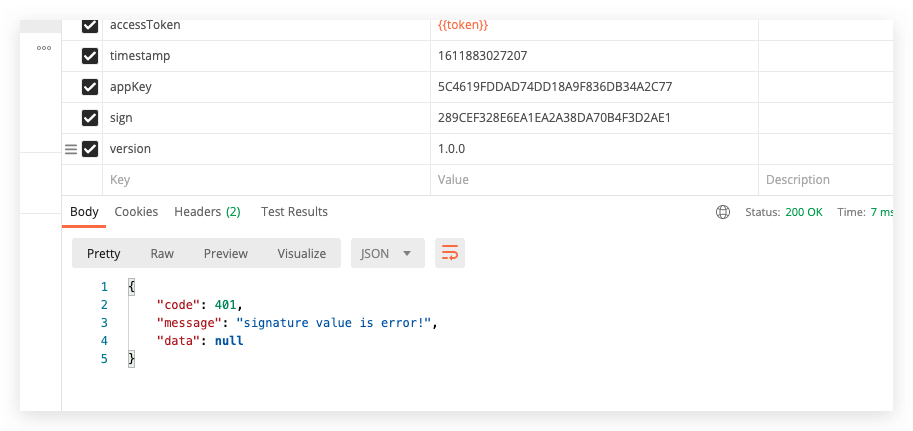 disable sign plug-in return
disable sign plug-in return 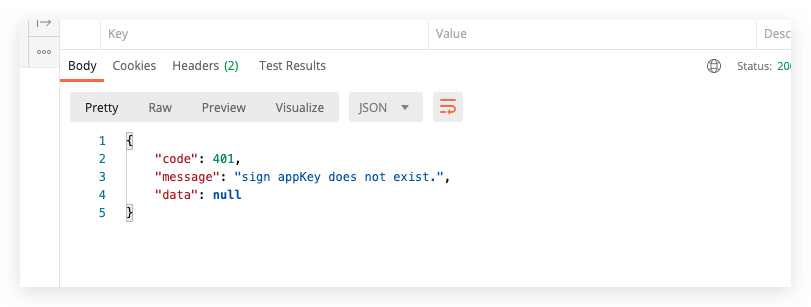
Implementation Analysis of sign Plug-in
Pair in Java
Simply speaking, pair stores a pair of key values, while map can store multiple pairs of key values. SignPlugin plug-in calls signVerify method in DefaultSignService to judge whether sign plug-in is available. If yes, obtain the soul Context stored in global plug-in and call verify method
if (signData != null && signData.getEnabled()) {
final SoulContext soulContext = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.CONTEXT);
assert soulContext != null;
return verify(soulContext, exchange);
}In the verify method, determine whether the request header information is correct. If not, throw the log. Error ( "sign parameters are incomplete, { }", soulContext) exception
if (StringUtils.isBlank(soulContext.getAppKey())
|| StringUtils.isBlank(soulContext.getSign())
|| StringUtils.isBlank(soulContext.getTimestamp())) {
log.error("sign parameters are incomplete,{}", soulContext);
return Pair.of(Boolean.FALSE, Constants.SIGN_PARAMS_ERROR);
}Judge whether the request time is timeout
if (between > delay) {
return Pair.of(Boolean.FALSE, String.format(SoulResultEnum.SING_TIME_IS_TIMEOUT.getMsg(), delay));
}Continue to call the sign method without timeout to get the authentication data, which is configured in soulAdmin
AppAuthData appAuthData = SignAuthDataCache.getInstance().obtainAuthData(soulContext.getAppKey());The appAuthData data will be judged later. If the data is wrong, the acquired parameters will not be re-signed to judge whether the incoming data is the same as the re-signed data.
String sigKey = SignUtils.generateSign(appAuthData.getAppSecret(), buildParamsMap(soulContext));If all the verification is passed, the authentication access request is completed.