One year later, the dromara team released version 2.1.1 of the new architecture Hmily distributed transaction framework
Thank you guys for your support all the way, and keep everyone waiting. In this version, our team refactored the entire project, reasonably divided functional modules, added configuration centers, adjusted the underlying storage structure, solved difficult bugs, and supported other new features, and absorbed more outstanding open source community members to join in.
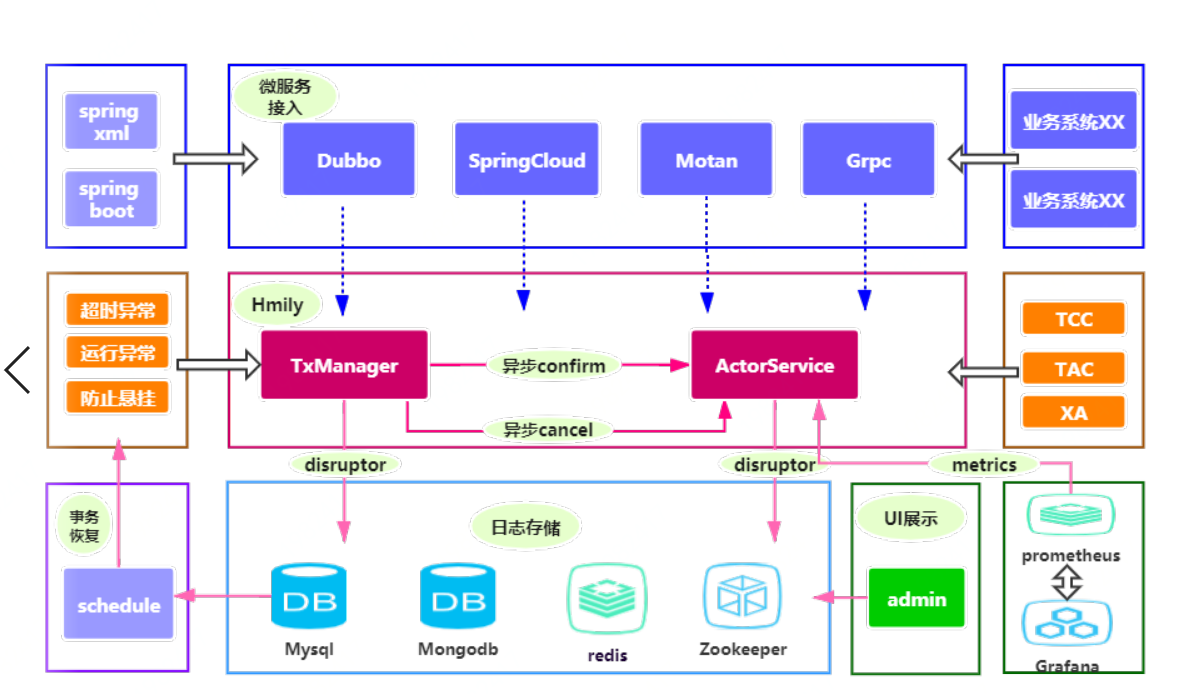
Architecture

Features
- High availability·: Supports abnormal transaction rollback and overtime transaction recovery in distributed scenarios to prevent transaction suspension.
- Ease of use: Provide zero-invasive Spring-Boot, Spring-Namespace to quickly integrate with business systems.
- High performance: Decentralized design, fully integrated with business systems, naturally supports cluster deployment.
- Observability: Performance monitoring of multiple metrics by Metrics, as well as admin management UI .
- Multiple RPCs: support Dubbo, SpringCloud, Motan, Sofa-rpc and other well-known RPC frameworks.
- Log storage: Support Mysql, Oracle, Mongodb, Redis, Zookeeper, etc.
- Complex scenarios: Support RPC nested call transactions.
Refactoring part
Module division:
- Extract the SPI custom module and It's open-the-box.
- SPI module that defines multiple storage methods for transaction logs.
- SPI module that defines multiple serialization methods for transaction logs.
- Add configuration center, support various mainstream configuration centers (Nacos, Apollo, Zookeeper, etc.), and support dynamic refresh of configuration.
- Add metrics module to monitor various information at runtime.
- Remove the core transaction execution module.
- Extract multiple RPC support modules.
- Extract the Spring and Spring Boot support modules.
On the dependent package version:
- Guava upgraded to 2.9.0.
- Curator upgraded to 5.1.0.
Code quality:
- Strict check-style code inspection, adhering to the principle of elegance and simplicity (talk is cheap, show you code).
openness :
- The community pursues the basic principles of simplicity, happiness, and harmony.
Goal:
- Create a high-availability, high-performance, easy-to-use financial-level distributed transaction solution.
Solve bugs:
- The Dubbo framework does not support the use of annotations (spring-boot-starter-dubbo).
- The Motan framework does not support the use of annotations.
- If Spring Cloud users use Feign and Hystrix to integrate Hmily, the thread switching problem occurs.
- In extreme cases, the transaction log serialization is abnormal.
- If timeout happen in
try, It will cause the transaction suspension bug. - When the
confirmandcancelphases are abnormal, the transaction fails to rollback. - In the transaction log storage, two modes of synchronous and asynchronous are supported for users to choose.
User guide
For Hmily users, it only takes three steps to achieve the BASE transaction between RPC service calls
- Add the maven dependencies supported by Hmily for various RPC.
- Add Hmily configuration.
- Add
@Hmilyannotation to RPC interface method.
Dependency changes
There is no change to the dependencies, only the version needs to be upgraded to 2.1.0. Here are examples of Dubbo microservices.
Dubbo RPC microservices
- Dubbo interface service dependency.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>hmily-annotation</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>- Dubbo service provider depends on version<2.7.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>hmily-dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
or
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dromara</groupId>
<artifactId>hmily-spring-boot-starter-dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>Hmily configuration changes
In the new version 2.1.0, the hmily-config module has been added to support local and registry modes. The user first needs to create a new file named hmily.yml under the project resouce file. The default path is the project's resource directory, it can also be specified with -Dhmily.conf, or the configuration can be placed in the user.dir directory. Priority level -Dhmily.conf> user.dir> resource. The file format is as follows (The local mode of configuration):
server:
configMode: local
appName: account-dubbo
config:
appName: account-dubbo
serializer: kryo
contextTransmittalMode: threadLocal
scheduledThreadMax: 16
scheduledRecoveryDelay: 60
scheduledCleanDelay: 60
scheduledPhyDeletedDelay: 600
scheduledInitDelay: 30
recoverDelayTime: 60
cleanDelayTime: 180
limit: 200
retryMax: 10
bufferSize: 8192
consumerThreads: 16
asyncRepository: true
autoSql: true
phyDeleted: true
storeDays: 3
repository: mysql
repository:
database:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url : jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/hmily?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password:
maxActive: 20
minIdle: 10
connectionTimeout: 30000
idleTimeout: 600000
maxLifetime: 1800000If you want to use Nacos as configuration center:
hmily:
server:
configMode: nacos
appName: xxxxx
remote:
nacos:
server: 192.168.3.22:8848
dataId: hmily.properties
group: DEFAULT_GROUP
timeoutMs: 6000
fileExtension: yml
passive: trueIf you want use Apollo as configuration center:
hmily:
server:
configMode: apollo
appName: xxxx
remote:
apollo:
appId: hmily-xxxxx
configService: http://192.168.3.22:8080
namespace: byin_hmily
secret:
fileExtension: yml
passive: true
env: dev
meta: http://192.168.3.22:808If you want to know more configuration methods and detailed explanations of configuration content, please refer to: https://dromara.org/zh-cn/docs/hmily/config.html .
Changes in the use of annotation methods
In the previous version, RPC interface and implementation only need to add @Hmily annotation, but now It need to be changed, you need to add @Hmily in the RPC interface method, which is used to identify this is a Hmily distributed transaction interface method , besides, you need to add @HmilyTCC to the implementation of the interface, and then specify the method names of confirm and cancel.
Example (say method in Dubbo needs to participate in distributed transactions):
public interface HelloService {
@Hmily
void say(String hello);
}
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@HmilyTCC(confirmMethod = "sayConfrim", cancelMethod = "sayCancel")
public void say(String hello) {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
public void sayConfrim(String hello) {
System.out.println(" confirm hello world");
}
public void sayCancel(String hello) {
System.out.println(" cancel hello world");
}
}Example (say method in springcloud needs to participate in distributed transactions):
- Spring-cloud service caller FeignClient.
@FeignClient(value = "helle-service")
public interface HelloService {
@Hmily
@RequestMapping("/helle-service/sayHello")
void say(String hello);
}- Spring-cloud provider.
@RestController
public class HelloController {
private final HelloService helloService ;
@Autowired
public AccountController(HelloService helloService) {
this.helloService= helloService;
}
@RequestMapping("/sayHello")
public void payment(String hello) {
return helloService.say(hello);
}
}
public interface HelloService {
void say(String hello);
}
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@HmilyTCC(confirmMethod = "sayConfrim", cancelMethod = "sayCancel")
public void say(String hello) {
System.out.println("hello world");
}
public void sayConfrim(String hello) {
System.out.println(" confirm hello world");
}
public void sayCancel(String hello) {
System.out.println(" cancel hello world");
}
}Changes in transaction log storage structure
Users don't need to care about using or upgrading, the framework will be initialized by default.
Next version
- Because of the adjustment of the architecture, it will be easier to support other modes. In the next version, TAC mode (try-auto-cancel) will be released, which will greatly simplify the use of the framework. You need only to care about the development of
confirmandcancelmethods, and It's provide better compatibility with the transformation of the old system. Don't worry about additional development tasks, just leave everything to Hmily! - It will support Brpc.
- It will support Tars-rpc.
Community
We uphold the principle of harmony and happiness. If you have ideas and want to contribute to community, come and join us!
- Github: https://github.com/dromara/hmily
- Gitee: https://gitee.com/dromara/hmily
- QQ group: 162614487