Sa-Token v1.42.0 Released: New API Key, TOTP Verification Codes, RefreshToken Lookup, and More
Sa-Token is a free, open-source, lightweight Java permission authentication framework designed to address a series of permission-related issues such as: login authentication, permission authentication, single sign-on (SSO), OAuth 2.0, and microservices gateway authentication. 🔐
The latest version, v1.42.0, has been pushed to the Maven Central Repository 🎉. You can include it in your project as follows:
<!-- Sa-Token Permission Authentication -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.dev33</groupId>
<artifactId>sa-token-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.42.0</version>
</dependency>This version includes a large number of ⛏️ new features, ⛏️ underlying refactorings, ⛏️ code optimizations, and more. Below are some of the more important updates for your reference:
🗝️ Update 1: New API Key Module
If you have ever integrated with open APIs from platforms like ChatGPT or DeepSeek, you are undoubtedly familiar with API Keys. 🤝
An API Key is an interface call credential, similar to a session token, but with more flexible permission control. 🔑
This update introduces full lifecycle management for API Keys, supporting the issuance, validation, disabling, and deletion of API Keys for specified accounts. Additionally, each API Key can be individually configured with different scope permissions, allowing the use of different API Keys in various scenarios to achieve key isolation and minimal authorization. 🛡️
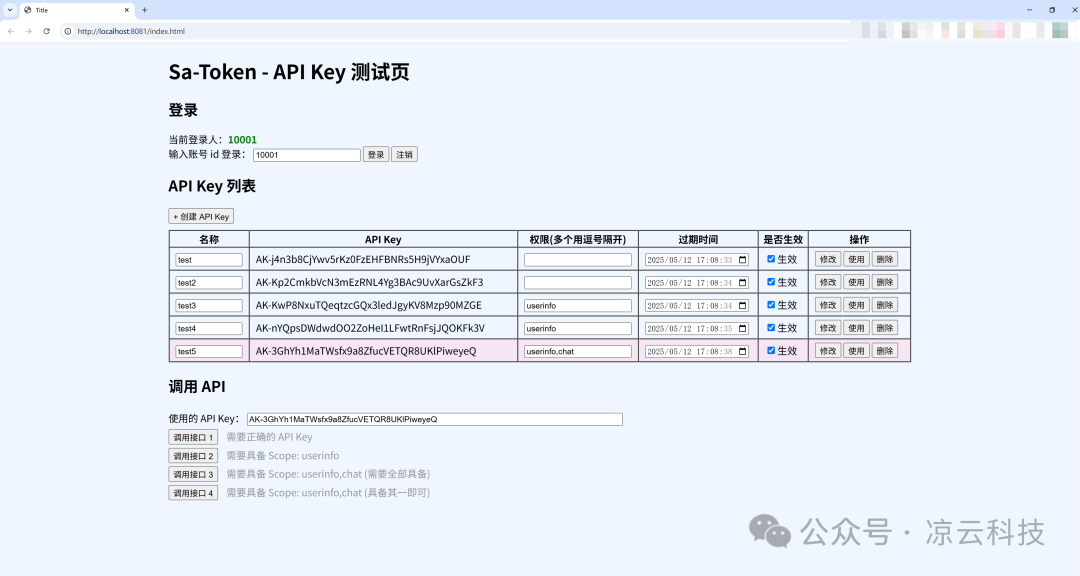
To better demonstrate the capabilities of this module, we have prepared a demo example:

sa-api-key
Example repository address: sa-token-demo-apikey 🔗
In this example, you can log in with different test accounts, issue API Keys for them, set scope permissions, and test API calls using different API Keys to observe the response results. 🧪
By default, the framework stores all API Key information in the cache, which can be referred to as "cache mode." In this mode, data will be lost after restarting the cache storage. ⚠️
The framework provides the SaApiKeyDataLoader interface, allowing you to switch data loading to "database mode" for long-term effective data storage. 💾
Direct link to online documentation: API Key Interface Call Credentials 🔗
🔍 Update 2: Refactored TempToken Module with Added Value Lookup Mechanism
In the Sa-Token documentation, there is an example like this: 📚
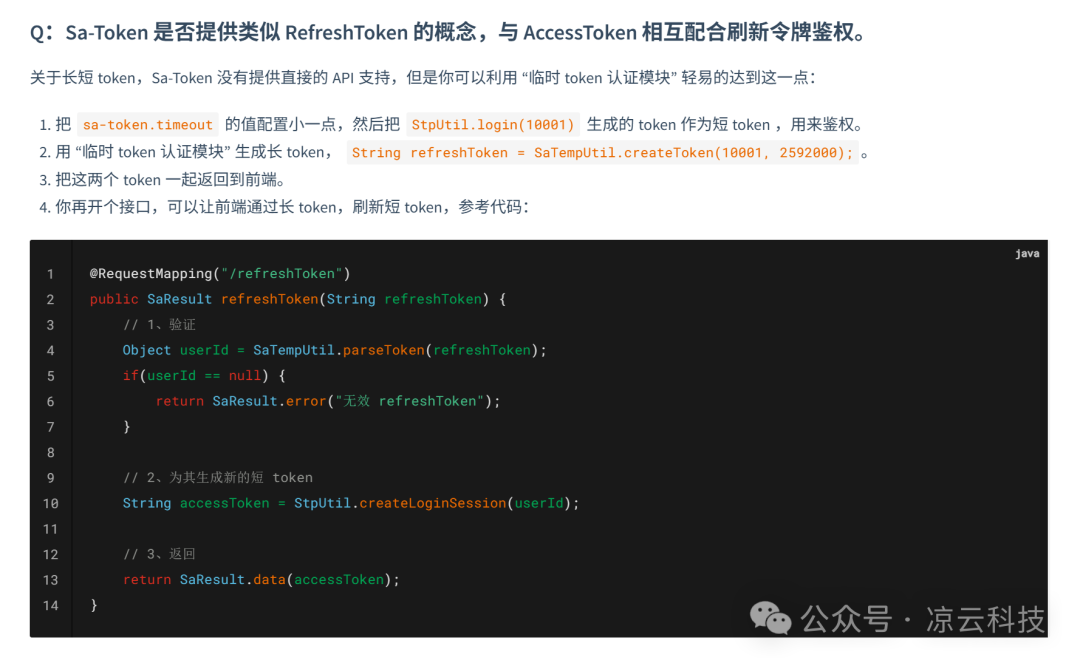
sa-refresh-token
This example demonstrates how to use the temporary Token authentication module to create a RefreshToken for a login session, achieving a dual-Token effect. 🔄
However, one day, I received a query from a user via the official Sa-Token assistant: 💬
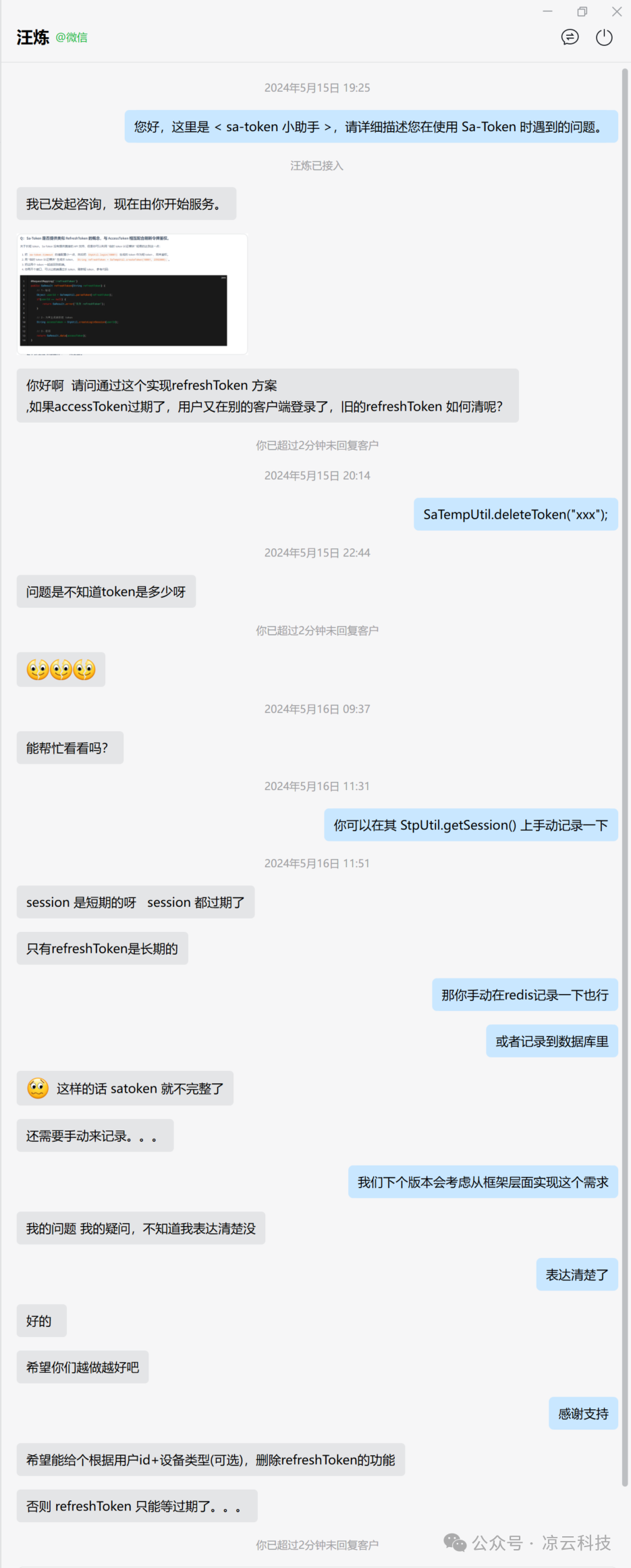
sa-refresh-token-wnglian-zixun
The user pointed out whether a lookup mechanism could be provided for RefreshToken to retrieve all historically issued RefreshTokens for a specific account.
Consider it done! 💪🏆
This version update allows the program to specify a third parameter when creating a refresh-token, indicating whether the framework should record Token index information:
SaTempUtil.createToken("10001", 2592000, true);Specifying false means no index is recorded, only the token is generated. Specifying true means index information is recorded, enabling future lookup of all historically issued tokens by value. 🔍
For example, we can use the SaTempUtil.getTempTokenList("xxx") method to retrieve all historically issued RefreshToken records for a specified account:
List<String> refreshTokenList = SaTempUtil.getTempTokenList("10001");Direct link to online documentation: Temporary Token Authentication 🔗
⏱️ Update 3: Added TOTP Algorithm Implementation
TOTP is a dynamic password algorithm used to generate short-lived numeric verification codes (typically 6-8 digits)️. Its core principle is to combine a secret key with the current time to generate a one-time password through a hash operation. ⏱
TOTP is generally used in the following scenarios:
- • 1. Two-factor authentication during login: After entering their username and password, users must also enter a TOTP verification code to log in successfully. 🔐
- • 2. Secondary authentication for sensitive operations: When performing high-risk sensitive operations, users need to enter a TOTP verification code to proceed. 🛡️
- • 3. Replacing SMS verification codes: TOTP verification codes can be generated offline without a network connection, to some extent replacing SMS verification codes for identity verification. 📴
This version adds functionality for generating and validating TOTP verification codes, making it easier for everyone to add two-factor authentication capabilities to their systems. 🚀
⚙️ Update 4: Refactored and Upgraded SaTokenContext Context Read/Write Strategy
This is likely the most low-level refactoring in recent versions, almost completely overhauling the previous design of the context module. 💥
In previous versions, Sa-Token needed to leverage the native context capabilities of different web frameworks to build its own context. 🌐
This update sees Sa-Token implementing its own context storage mechanism using ThreadLocal, which brings the following benefits:
- • 1. Easier and simpler integration with more web frameworks.
- • 2. Ability to temporarily mock a context in asynchronous scenarios to call Sa-Token's synchronous APIs.
- • 3. Complete removal of the secondary context module, achieving context unification between web requests and RPC requests.
- • 4. Sa-Token synchronous APIs can now be called within firewall hooks.
🌐 Update 5: Added CORS Cross-Origin Strategy Handler, Providing a Unified Cross-Origin Solution Across Different Architectures
In previous versions, cross-origin processing always had to be written in the global authentication filter, treated as an "additional supplementary operation under authentication." ⏳
The new version specifically provides a CORS cross-origin handling strategy component. You no longer need to write a lengthy authentication filter component just for cross-origin handling. 🚀
/**
* CORS Cross-Origin Handling
*/
@Bean
public SaCorsHandleFunction corsHandle() {
return (req, res, sto) -> {
res.
// Allow specified origins to access cross-origin resources
setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*")
// Allow all request methods
.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST, GET, OPTIONS, DELETE")
// Validity period
.setHeader("Access-Control-Max-Age", "3600")
// Allowed header parameters
.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "*");
// If it's a preflight request, return immediately to the frontend
SaRouter.match(SaHttpMethod.OPTIONS)
.free(r -> System.out.println("--------OPTIONS preflight request, no processing"))
.back();
};
}Open-source repository example: sa-token-demo-cross 🔗
🔑 Update 6: sa-token-quick-login Plugin Now Supports Authentication via Http Basic
sa-token-quick-login can quickly and conveniently add a login page to your project. After adding the dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.dev33</groupId>
<artifactId>sa-token-quick-login</artifactId>
<version>1.42.0</version>
</dependency>Starter Class:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SaTokenQuickDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SaTokenQuickDemoApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("\n------ Startup Successful ------");
System.out.println("name: " + SaQuickManager.getConfig().getName());
System.out.println("pwd: " + SaQuickManager.getConfig().getPwd());
}
}Test Controller:
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping({"/", "/index"})
public String index() {
String str = "<br />"
+ "<h1 style='text-align: center;'>Resource Page (Login Required to Access This Page) </h1>"
+ "<hr/>"
+ "<p style='text-align: center;'> Sa-Token " + SaTokenConsts.VERSION_NO + " </p>";
return str;
}
}Start the project and access it using a browser: http://localhost:8081. The first visit will redirect you to the login page since you are not logged in 🚪:
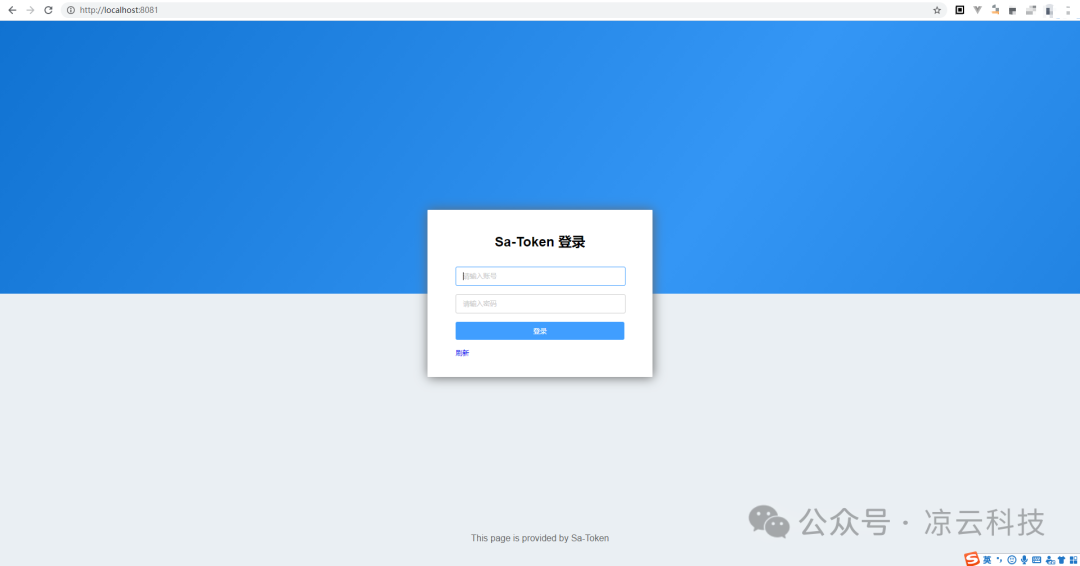
Login
Use the default account: sa / 123456 to log in, and you will see the resource page.
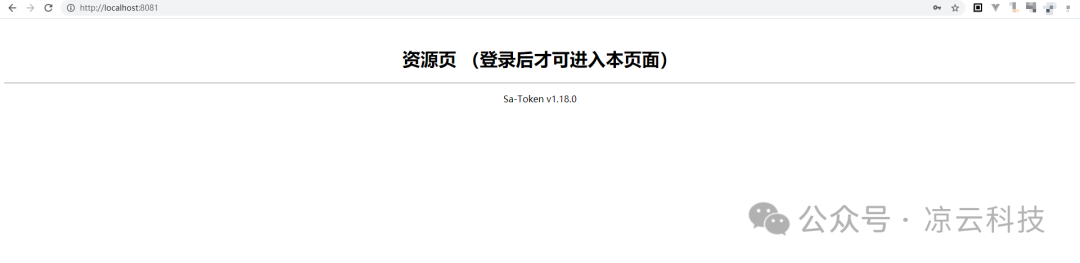
Logged In
The new version adds the ability to authenticate directly via Http Basic:
http://sa:123456@localhost:8081/This will be very helpful for testing quick-login related resource interfaces in dedicated API testing tools. 🧪
📜 Full Changelog
In addition to the points mentioned above, there are more updates that cannot be detailed one by one. Below is the complete changelog for version v1.42.0:
• core:
- • Added: New
API Keymodule. [Important] - • Added: New
TOTPimplementation. [Important] - • Refactor: Refactored
TempTokenmodule, added value lookup mechanism for tokens. [Important] - • Upgrade: Refactored and upgraded
SaTokenContextcontext read/write strategy. [Important] - • Added: New Mock context module. [Important]
- • Removed: Removed secondary context module.
- • Added: New demo for usage in asynchronous scenarios. [Important]
- • Added: New
Base32encoding utility class. - • Added: New
CORScross-origin strategy handler, providing a unified cross-origin solution across different architectures. - • Added:
renewTimeoutrenewal method now includes token terminal information validity check. - • Added: Global configuration item
cookieAutoFillPrefix: whether to automatically fill the token prefix in cookie mode. - • Added: Global configuration item
rightNowCreateTokenSession: whether to immediately create the correspondingToken-Sessionupon login. - • Optimization: Optimized
Token-Sessionretrieval algorithm to reduce cache read次数. - • Added:
SaLoginParametersupports configuringSaCookieConfigfor Cookie-related parameters. - • Modified: The registration order of the firewall validation filter changed to -102.
- • Added: Firewall
hookregistration新增registerHookToFirst,registerHookToSecondmethods for more flexible control of hook order.
- • Added: New
• Plugins:
- • Added:
sa-token-quick-loginplugin now supports authentication viaHttp Basic.
- • Added:
• Unit Tests:
- • Completion: Added unit tests for the
Temp Tokenmodule.
- • Completion: Added unit tests for the
• Documentation:
- • Completion: Updated the list of sponsors.
- • Fix: Fixed incorrect dependency example description in the
Thymeleafintegration documentation. - • Fix: Fixed erroneous description in the
unionidsection. - • Optimization: Optimized the SSO Mode三 single sign-out steps with more detailed descriptions.
- • Added: Added Cookie viewing step demonstration diagram to the login authentication documentation.
- • Added: Added a note in the multi-account mode:
LoginTypecannot be changed at runtime. - • Added: Added QA for multi-account mode: determining which system's account is currently logged in within an interface.
- • Added: Added QA: resolving errors when introducing Sa-Token in lower versions of
SpringBoot (<2.2.0). - • Added: Added QA: In integrated frontend-backend projects, how to return to the original page after login when redirected to the login page due to interception for not being logged in?
- • Added: Added QA: How to cluster Sa-Token integrated with Redis?
- • Added: Added QA: How to customize the way the framework reads tokens?
- • Added: Added QA: Troubleshooting possible reasons why modifying the
hostsfile is ineffective. - • Added: Added QA: How to prevent CSRF attacks.
- • Added: New chapter: "Asynchronous & Mock Context".
- • Upgrade: Upgraded the "Custom SaTokenContext Guide" chapter documentation.
Direct link to the online changelog documentation: https://sa-token.cc/doc.html#/more/update-log
🌟 Other
Code repository address: https://gitee.com/dromara/sa-token
Framework functional structure diagram: